See Two Tricky Occultations — Neptune and Lambda (λ) Aqr

On July 22-23, the waning gibbous moon occults Neptune, here shown during its simulated reappearance. The planet's tiny 2.3″ aqua disk is dwarfed by the Moon.
Stellarium
Stellarium
I love magic. It always makes me feel so dumb. That's probably because I'm terrible at figuring out magic tricks. Levitating tables? Death saw? Keep 'em coming! A favorite trick is to make a quarter disappear and then pull it out of someone's ear, a ruse that finds its counterpart in the night sky.
On Friday night–Saturday morning July 22-23, the magician Moon performs a classic magic act when it will make both Neptuneand Lambda (λ) Aquariidisappear for about an hour (or less depending on your location) and then return them to view no harm done. Because the Moon will be 88% illuminated at the time, seeing the bright side disappearance will be relatively easy for the star, which shines at magnitude +3.7, but all but impossible for Neptune at +7.8.

This color-coded map shows where the Neptune occultation will be visible. Cyan = occultation at moonrise/moonset; red dotted = daytime occultation; blue = twilight occultation; and white = nighttime occultation. Click the image for a list of cities and times of the planet's reappearance at the Moon's dark limb.
Occult 4.1
Occult 4.1
Fortunately, both will be visible during their reappearance at the moon's dark limb. A small scope will show the star, but you'll need an 8-inch or larger telescope with clean optics (to minimize scattered light) to nab the planet. Even then it will be a challenge. Both occultations occur within about a half hour of each other with Neptune going first. Interestingly, since both objects are just 30′ apart on that night, the Moon almost glides right between them. But not quite. Because the Moon is near perigee with a diameter of 32′ that evening, it either occults one and narrowly misses the other, or occults both!

Here's the view from three different cities: Quebec, Chicago, and Jackson, Mississippi. Times noted are when Neptune reappears at the Moon's dark limb at lower right. Jackson is far enough south that the Moon also occults Lambda Aqr (hidden).
Maps: Bob King; Source: Stellarium
Maps: Bob King; Source: Stellarium
What you'll see depends on your location, which causes the Moon's apparent position to shift this way or that against the more distant background stars, a phenomenon called parallax. Since we're mostly interested in the reappearances of the star and planet, we'll focus on that aspect of the occultation. Neptune returns to view along the Moon's southeastern limb (southwest side in "Earth" directions) around 5:35 UT or 12:35 a.m. EDT July 23rd from many locations across the eastern two-thirds of North America (except Florida).

From Atlanta, both Neptune and Lambda Aqr will reappear at 12:24 a.m. and 12:38 a.m. EDT, respectively, after being occulted by the Moon.
Map: Bob King; Source: Stellarium
Map: Bob King; Source: Stellarium
Observers on a line from central Texas through central Louisiana and across southern Mississippi, Alabama, and Georgia will witness a grazing occultation, with Neptune scraping along the moon's southern limb.
Not long after the Moon covers Neptune, it will also occult Lambda Aqr for observers in the southern states, Central America, and northern South America. Disappearance will take place around 4:30 UT (11:30 EDT) and reappearance about 5:45 UT (12:45 EDT).
The northern graze line cuts across northern New Mexico and continues through central Oklahoma, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Anywhere north of this line, the Moon misses Lambda, passing just below the star. Skywatchers living south of the Lambda's graze line and north of Neptune's get to see both reappearances!
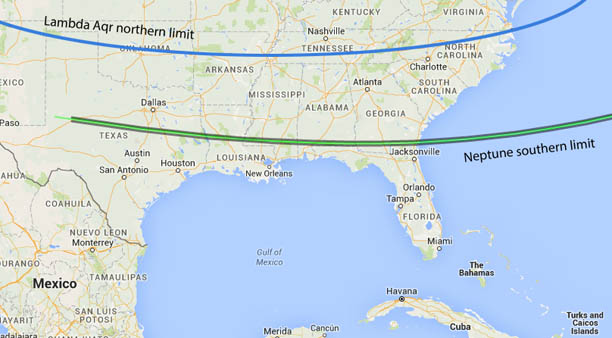
This map shows the visibility limits for the reappearances of Neptune and Lambda Aqr at the Moon's dark limb after occultation. South of the Neptune limit, the planet won't be occulted; north of the Lambda limit, the star won't be occulted. Both will be occulted and reappear at the Moon's dark limb for observers living between the two limits.
Bottom curve and map: David Dunham, David Herald, Occult software; top curve adapted from the Curt Renz map
Bottom curve and map: David Dunham, David Herald, Occult software; top curve adapted from the Curt Renz map
What to do if you live in the western U.S. and Canada where the Moon doesn't rise until well after Neptune's reappearance? Use the opportunity to make easy work of finding Neptune. You'll spot it just ½° to ¾° due west of the Moon. For that matter, observers in the far southern U.S., where no occultation will occur, can still use the Moon to find the planet, located a few arcminutes south-southwest of the lunar limb. Neptune displays a pale blue disk through a 4-inch and larger telescopes when viewed at 100x or higher.
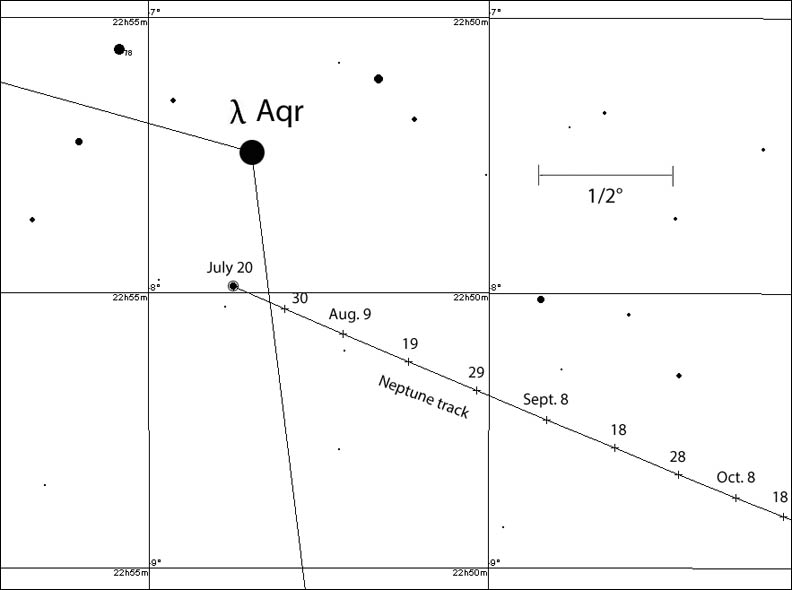
Use this map to keep track of Neptune's whereabouts through mid-October as it ambles southeastward from Lambda Aqr. Positions are shown for 11 p.m. CDT every 10 days. Stars shown to magnitude +9.5. North is up.
Chris Marriott's SkyMap software
Chris Marriott's SkyMap software
Once the Moon departs the area two nights later, Neptune remains within about ½° of Lambda through month's end, making it an easy catch in telescopes and binoculars any clear night. Center Lambda in your low power telescopic field of view and the pale blue planet will appear a short distance to the SSW. With a 10-inch or larger telescope and magnification of around 200x, try digging out Neptune's brightest moon Triton at magnitude +14. It's not as hard you might think! To help pinpoint its location and confirm your observation check out Sky &Telescope's Triton Tracker. You can also download S&T's Neptune finder chart to track the ice giant into the fall and winter.
Even though the solar system's most remote planet comes to opposition on September 2nd, let yourself get swept up in some Neptunian magic early. The occultation also serves as a preview for a striking dawn conjunction and occultation of Aldebaran by the crescent Moon on July 29th. Clear skies!
No comments:
Post a Comment